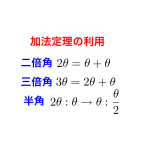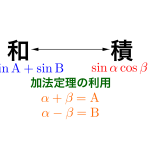こんにちは、リンス(@Lins016)です。
今回は三角関数の公式まとめについて学習していこう。
三角関数の公式の一覧と覚えるものと導くもの
三角関数は本当に覚える公式が多いから大変だよね。定期試験で三角関数が試験範囲なら全部覚えて試験に臨むと思うけど、実力試験や入試になるとたまにしか出てこない公式を全部覚えてるのって難しいよね。
もちろん全部覚えてるのがベストだけど、覚えたつもりで符号間違いとか一番最悪だから、完全に覚えきれない人は、必要最低限の公式をきちんと覚えて、それを利用して他の公式を導くことを覚えよう。
・三角関数の相互関係式
・余角・補角などの還元公式
・三角関数の周期性・対称性
・加法定理
・二倍角・半角・三倍角の公式
・和積・積和の公式
・三角関数の合成
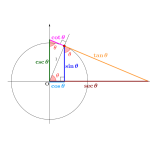
三角関数の相互関係式
\(\small{ \ \sin\theta \ }\)か\(\small{ \ \cos\theta \ }\)か\(\small{ \ \tan\theta \ }\)のどれか一つの三角関数が与えられたときに、残りの三角関数を求めるときに使おう。
\(\small{ \ \sin^2\theta+\cos^2\theta=1 \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \tan\theta=\displaystyle\frac{\sin\theta}{\cos\theta} \ }\)
\(\small{ \ 1+\tan^2\theta=\displaystyle\frac{1}{\cos^2\theta} \ }\)
余角・補角などの還元公式
この式は数学Ⅰの三角比でも学習したけど、加法定理を使って導けるから加法定理を覚えて加法定理で値を求めよう。いちいち単位円を書いたりしなくてもいいからね。
\(\small{ \ \sin\left(\displaystyle\frac{\pi}{2}-\theta\right)=\cos\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos\left(\displaystyle\frac{\pi}{2}-\theta\right)=\sin\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \tan\left(\displaystyle\frac{\pi}{2}-\theta\right)=\displaystyle\frac{1}{\tan\theta} \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \sin\left(\displaystyle\frac{\pi}{2}+\theta\right)=\cos\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos\left(\displaystyle\frac{\pi}{2}+\theta\right)=-\sin\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \tan\left(\displaystyle\frac{\pi}{2}+\theta\right)=-\displaystyle\frac{1}{\tan\theta} \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \sin(\theta+\pi)=-\sin\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos(\theta+\pi)=-\cos\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \tan(\theta+\pi)=\tan\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \sin(\pi-\theta)=\sin\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos(\pi-\theta)=-\cos\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \tan(\pi-\theta)=-\tan\theta \ }\)
-

三角比の相互関係と値の求め方
余角や補角の三角比や三角比の値の求め方について詳しく解説しています。
続きを見る
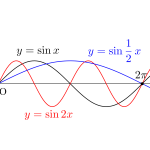
三角関数の周期性
三角関数は周期関数だから周期ごとに同じ値になるよね。
\(\small{ \ \sin\left(\theta+2n\pi\right)=\sin\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos\left(\theta+2n\pi\right)=\cos\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \tan\left(\theta+n\pi\right)=\tan\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \sin\theta, \ \cos\theta \ }\)の周期は\(\small{ \ 2\pi \ }\)、\(\small{ \ \tan\theta \ }\)の周期は\(\small{ \ \pi \ }\)だからそれぞれ周期の\(\small{ \ n \ }\)倍を加えても同じ値になるんだ。
合わせて各グラフについても確認しておこう。
三角関数の対称性
単位円から考えてもいいし、グラフの対称性(奇関数・偶関数)から考えてもいい。
\(\small{ \ \sin(-\theta)=-\sin\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos(-\theta)=\cos\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \tan(-\theta)=-\tan\theta \ }\)
-

三角関数のグラフ(1)
sinとcosのグラフの注意する点について詳しく解説しています。
続きを見る
-

三角関数のグラフ(2)
tanのグラフの漸近線の求め方や平行移動について詳しく解説しています。
続きを見る
加法定理
加法定理は三角関数の中で一番重要な公式だよね。とりあえずこれさえ覚えておけば何とかなる。でも、その他の公式も加法定理をどう使って導くのか知っておかないといけないよ。
\(\small{ \ \sin\left(\alpha+\beta\right)=\sin\alpha\cos\beta+\cos\alpha\sin\beta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos\left(\alpha+\beta\right)=\cos\alpha\cos\beta-\sin\alpha\sin\beta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \tan\left(\alpha+\beta\right)=\displaystyle\frac{\tan\alpha+\tan\beta}{1-\tan\alpha\tan\beta} \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \alpha-\beta \ }\)は\(\small{ \ \beta \ }\)を\(\small{ \ -\beta \ }\)に変えた式だから上の式をそれぞれ\(\small{ \ \sin(-\beta)=-\sin\beta \ }\)、\(\small{ \ \cos(-\beta)=\cos\beta \ }\)、\(\small{ \ \tan(-\beta)=-\tan\beta \ }\)に変えると導けるよね。
\(\small{ \ \sin\left(\alpha-\beta\right)=\sin\alpha\cos\beta-\cos\alpha\sin\beta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos\left(\alpha-\beta\right)=\cos\alpha\cos\beta+\sin\alpha\sin\beta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \tan\left(\alpha-\beta\right)=\displaystyle\frac{\tan\alpha-\tan\beta}{1+\tan\alpha\tan\beta} \ }\)
でもこの式は導くよりもきちんと覚えておこう。 加法定理の証明方法は色々ありますが、単位円を利用した一般的な証明を学習します。 続きを見る

加法定理の証明
二倍角の公式
加法定理に\(\small{ \ \alpha=\beta=\theta \ }\)を代入した式から二倍角の式が導けるんだけど、非常によく使う式だから覚えておこう。
\(\small{ \ \sin2\theta=2\sin\theta\cos\theta \ }\)
\(\small{\begin{eqnarray}\cos2\theta&=&\cos^2\theta-\sin^2\theta\\
&=&1-2\sin^2\theta\\
&=&2\cos^2\theta-1 \ \end{eqnarray}}\)
\(\small{ \ \tan2\theta=\displaystyle\frac{2\tan\theta}{1-\tan^2\theta} \ }\)
半角の公式
二倍角の公式の\(\small{ \ \cos2\theta \ }\)の式から半角の公式を導こう。
\(\small{ \ \sin^2\displaystyle\frac{\theta}{2}=\displaystyle\frac{1-\cos\theta}{2} \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos^2\displaystyle\frac{\theta}{2}=\displaystyle\frac{1+\cos\theta}{2} \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \tan^2\displaystyle\frac{\theta}{2}=\displaystyle\frac{1-\cos\theta}{1+\cos\theta} \ }\)
三倍角の公式
加法定理に\(\small{ \ \alpha=2\theta, \ \beta=\theta \ }\)を代入して導こう。\(\small{ \ \sin3\theta \ }\)は\(\small{ \ \sin\theta \ }\)だけで、\(\small{ \ \cos3\theta \ }\)は\(\small{ \ \cos\theta \ }\)だけで表せることを覚えておこう。
\(\small{ \ \sin3\theta=3\sin\theta-4\sin^3\theta \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos3\theta=4\cos^3\theta-3\cos\theta \ }\)
-

二倍角・半角・三倍角の公式の求め方
加法定理を利用した証明方法について解説しています。
続きを見る
和積の公式
加法定理から導こう。\(\small{ \ \tan \ }\)に関する式はないから覚えておこう。
\(\small{ \ \sin\alpha\cos\beta=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\left\{\sin\left(\alpha+\beta\right)+\sin\left(\alpha-\beta\right)\right\} \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos\alpha\sin\beta=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\left\{\sin\left(\alpha+\beta\right)-\sin\left(\alpha-\beta\right)\right\} \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos\alpha\cos\beta=\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\left\{\cos\left(\alpha+\beta\right)+\cos\left(\alpha-\beta\right)\right\} \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \sin\alpha\sin\beta=-\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}\left\{\cos\left(\alpha+\beta\right)-\cos\left(\alpha-\beta\right)\right\} \ }\)
積和の公式
加法定理から導こう。\(\small{ \ \tan \ }\)に関する式はないから覚えておこう。
\(\small{ \ \sin \mathrm{A}+\sin\mathrm{B}=2\sin\displaystyle \frac{\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}}{2}\cos\displaystyle \frac{\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{B}}{2} \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \sin \mathrm{A}-\sin\mathrm{B}=2\cos\displaystyle \frac{\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}}{2}\sin\displaystyle \frac{\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{B}}{2} \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos \mathrm{A}+\cos\mathrm{B}=2\cos\displaystyle \frac{\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}}{2}\cos\displaystyle \frac{\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{B}}{2} \ }\)
\(\small{ \ \cos \mathrm{A}-\cos\mathrm{B}=-2\sin\displaystyle \frac{\mathrm{A}+\mathrm{B}}{2}\sin\displaystyle \frac{\mathrm{A}-\mathrm{B}}{2} \ }\)
-

和積の公式と積和の公式の求め方
加法定理を利用した和積の公式と積和の公式の求め方について解説しています。
続きを見る
三角関数の合成
\(\small{ \ \sin \ }\)と\(\small{ \ \cos \ }\)の偏角が同じものの和や差は合成を使って一つにまとめよう。偏角が同じなら係数が違っても構わない。
\(\small{ \ a\sin\theta+b\cos\theta=R\sin\left(\theta+\alpha\right) \ }\)
ここで\(\small{ \ \alpha \ }\)は\(\small{ \ \sin\alpha=\displaystyle\frac{b}{\sqrt{a^2+b^2}}, \ \cos\alpha\displaystyle\frac{a}{\sqrt{a^2+b^2}} \ }\)
合成のやり方は確実にマスターしよう。 sinの合成だけでなくcosの合成についても詳しく解説しています。 続きを見る
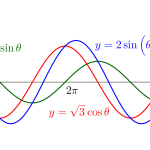
三角関数の合成
Point 三角関数の公式まとめ
①すべての公式を使えるようにする
②相互関係式・加法定理は確実に覚える
③あまり利用しない公式は覚えなくても導けるようにしておく